Monday, April 18, 2011
Sunday, April 10, 2011
Poll question of week 10
Based of the result of the poll question, there is a total of 45 votes and 4 (8%) votes the purpose of the phisher is hacking for fun. Some of people think the phisher are bored people looking for amusement. The people think the phisher break in because they think somebody might have interesting data and they have nothing better to do. The phisher have a strong desire to know about how to phishing attack and they often damage the something through ignorance or in trying to cover their tracks.
3 (6%) votes the purpose of the phisher is to do damage. A few of people think the phisher out to do damage, either because they get their kicks from destroying things. The phisher just want to damage something which makes it less attractive, useful or valuable. Only 2 (4%) votes the phisher do not like somebody. Not many people think phisher are do not like somebody because they are anger somebody become a target to phishing attack.
Most of people 22 (48%) votes phisher break in because they are want information for other purpose. While these phisher are not above theft, they usually steal things that are directly convertible into money or further access such as credit card, telephone, or network access information. If they find secrets they think they can sell, they may try to do so, but that's not their main business.
14 (31%) votes the purpose of the phisher is prefer sites of particular interest. A lot of people think phisher may prefer sites of particular interest. Breaking into something well-known, well-defended, or otherwise especially neat is usually worth more points to them. However, they will also attack anything they can get at; they are going for quantity as well as quality. They do not have to want anything you have got, or care in the least about the characteristics of your site. They may or may not do damage on the way through. They will certainly gather information and keep it for phishing attack.
Monday, April 4, 2011
Sunday, April 3, 2011
Crossword Puzzle Winner


Saturday, April 2, 2011
Poll question of week 9
Sunday, March 27, 2011
Poll question of week 8
Phishing Contest
Phishing Contest !!
Name:
Age:
Gender:
Email address:
Rule:
1.Your information submitted must be truth.
2.We have the capability to cancel your qualifications, if found any cheater.
3.No copy from your friend.
4.Must be Malaysian.
5.Pass up before the deadline.
Thursday, March 24, 2011
Japan Earthquake Scam ?
Link to us: http://snipurl.com/japanearthquakescam
Scammers and hackers are using the devastating earthquake and tsunami in Japan to appeal for fraudulent charity donations. US-CERT, the operational arm of the National Cyber Security Division (NCSD) at the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), is warning users regarding fake antivirus and phishing attacks regarding the Japan earthquake and the tsunami disasters. Scammers are also flooding e-mail inboxes with messages asking recipients to donate money to relief efforts.
In Facebook also scams are rocking, If you get a link to something like “Japanese Tsunami RAW Tidal Wave Footage’, don’t click it. It’s a scam. You may be tricked into “liking” the page and then taking a personal info harvesting survey, and then promoting the scam.
Symantec has observed a classic 419 message targeting the Japanese disaster, said researcher Samir Patil in a post to the company’s security blog. “The message is a bogus ‘next of kin’ story that purports to settle millions of dollars owing to an earthquake and tsunami victim.” Hackers have also registered a large number of domains with URLs that may fool users into thinking that they’re legitimate donation or relief sites, said Patil, a tactic that can also push those sites higher on search results.
How to Protect yourself
- Do not follow unsolicited web links or attachments in email messages.
- Maintain up-to-date antivirus software.
- Verify the legitimacy of the email by contacting the organization directly through a trusted contact number.
- Pay attention to the URL of a website. Malicious websites may look identical to a legitimate site, but the URL may use a variation in spelling or a different domain.
- Take advantage of any anti-phishing features offered by your email client and web browser.
Sunday, March 20, 2011
Poll question of week 7
Based on the result of the poll question, there is a total of 36 votes and 31(83%) votes the paypal phishing will affects customers online purchased. According the top 10 phishing websites in 2010, the paypal phishing is one of the most popular in the word. Most of people think that victims may be to click on the link in the e-mail which leads the victims to a fake website; this is serious problem for customers online purchased. Only 6 (16%) votes the paypal phishing will not be affect customers online purchased. A few of people are think the people having a lot of experience of the world and knowing about phishing and they do not worry about it.
Thursday, March 17, 2011
Avoid Japan Earthquake Phishing
1) Check for the URL spelling. Hackers are smart at making the fake URL looks real, for instance, credits.com for credit.com. This technique is called typosquatting.
2) Do not get misdirected. Online financial phishing scams will frequently direct you to a third party website that ask for your credit card information. If you’re being redirected to another site that does not look right, please disconnect from that website. Do not pay any attention to the link text because they can say anything. You have to pay more attention to the URL.
3) Avoid the social pressure. A scams usually works because it preys on a huge amount of people, please do some research if you see a website that appears syspicious. Never trust messages and links spread through Twitter.com and Facebook.com because they are hotbeds for scammers looking to mkake quick cash. Never give out your PIN code, driver's lisence number, phone number or date of birth because none of that information is required by legitimate sites like Red Cross.
Monday, March 14, 2011
Announcement :: Crossword Puzzle coming out soon !
Name:
Gender:
Age:
Email Address:
Current Location:
Poll Week 6
Saturday, March 12, 2011
Phone Phishing
There is another type of phishing - phone phishing. This happens when someone pretending to be from a government agency or company, trying to ask for your personal information. It sounds easy to avoid, but unfortunately these people only need a few victims to fall for the scam to make it profitable.
Phone phishing is increasing. Sometimes it seems like your bank is really calling you. Phone phisher can assume your identity and empty your bank accounts. Here are some things you need to remember when conducting sensitive financial transactions over the phone:
1) Never give out full account numbers. Your financial institution doesn't need account numbers to verify your identity, if it is really necessary, give last four digits only, or insist on other methods to verify your identity, such as your date of birth.
2) Do not call a number left in a recording. Instead, you should call the known customer service for your bank. Although you may need to go through a couple of transfer, at least it is safer.
3) Be aware of repeated recordings to get a hold of you about important account or personal information. The bank is likely to use a real person to call you if there is really a problem.
4) Do not trust caller ID because it can be spoofed. It is important to find out the exactly spelling and words that should appear on caller ID from your bank's customer service number.
Have you been a victim of phone phishing?
Reference:
1)All Business [Online], Retrieved 11 March 2011
URL: http://www.allbusiness.com/crime-law-enforcement-corrections/criminal-offenses/14808871-1.html
2)Internet Fraud Tips [Online], Retrieved 11 March 2011
URL: http://www.fraud.org/tips/internet/phishing.htm
Monday, March 7, 2011
Poll week 5
Friday, March 4, 2011
Top 10 Phishing Website in 2010.
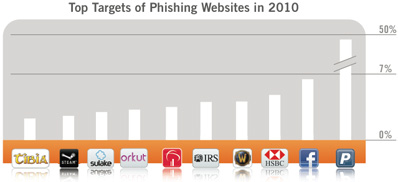
1. PayPal — 45.9%1.
2. Facebook — 5.3%2.
3. HSBC Group — 4.1%3.
4. World of Warcraft — 3.2%4.
5. Internal Revenue Service — 3%5.
6. Bradesco — 1.9%6.
7. Orkut — 1.7%7.
8. Sulake Corporation — 1.5 %8.
9. Steam — 1.2%9.
10. Tibia — 1%10.
In OpenDNS annual report for 2010, the most frequently phished website in every month of 2010 was Paypal, which is 9 times more than the second popular phisher target, Facebook (5.3% fake sites). Five of the top ten phished website (Facebook, World of Warcraft, Sulake Corporation, Steam and Tibia are associated with social and online games.
References
Help Net Security [Online], Retrieved on 10 March 2011.
URL: http://www.net-security.org/secworld.php?id=10487
Thursday, March 3, 2011
New phishing technique exploits browser tab use
Monday, February 28, 2011
Poll question week 4

Poll question week four: Did you check your URL everytime when you access to website?There is a total of 12 votes, 8 of them voted "Yes", 4 of them voted "Sometimess", and none of them voted "No". The poll make us know that majority of them beware of phishing. To avoid be the victim of phishers, we should always check the URL of the website you accessing.
Sunday, February 27, 2011
Type of Phishing Attack
Link to us: http://snipurl.com/typeofphishingattack
Deceptive Phishing. The term "phishing" originally referred to account theft using instant messaging but the most common broadcast method today is a deceptive email message. Messages about the need to verify account information, system failure requiring users to re-enter their information, fictitious account charges, undesirable account changes, new free services requiring quick action, and many other scams are broadcast to a wide group of recipients with the hope that the unwary will respond by clicking a link to or signing onto a bogus site where their confidential information can be collected.
Malware-Based Phishing refers to scams that involve running malicious software on users' PCs. Malware can be introduced as an email attachment, as a downloadable file from a web site, or by exploiting known security vulnerabilities--a particular issue for small and medium businesses (SMBs) who are not always able to keep their software applications up to date.
Keyloggers and Screenloggers are particular varieties of malware that track keyboard input and send relevant information to the hacker via the Internet. They can embed themselves into users' browsers as small utility programs known as helper objects that run automatically when the browser is started as well as into system files as device drivers or screen monitors.
Session Hijacking describes an attack where users' activities are monitored until they sign in to a target account or transaction and establish their bona fide credentials. At that point the malicious software takes over and can undertake unauthorized actions, such as transferring funds, without the user's knowledge.
Web Trojans pop up invisibly when users are attempting to log in. They collect the user's credentials locally and transmit them to the phisher.
Hosts File Poisoning. When a user types a URL to visit a website it must first be translated into an IP address before it's transmitted over the Internet. The majority of SMB users' PCs running a Microsoft Windows operating system first look up these "host names" in their "hosts" file before undertaking a Domain Name System (DNS) lookup. By "poisoning" the hosts file, hackers have a bogus address transmitted,taking the user unwittingly to a fake "look alike" website where their information can be stolen.
System Reconfiguration Attacks modify settings on a user's PC for malicious purposes. For example: URLs in a favorites file might be modified to direct users to look alike websites. For example: a bank website URL may be changed from "bankofabc.com" to "bancofabc.com".
Data Theft. Unsecured PCs often contain subsets of sensitive information stored elsewhere on secured servers. Certainly PCs are used to access such servers and can be more easily compromised. Data theft is a widely used approach to business espionage. By stealing confidential communications, design documents, legal opinions, employee related records, etc., thieves profit from selling to those who may want to embarrass or cause economic damage or to competitors.
DNS-Based Phishing ("Pharming"). Pharming is the term given to hosts file modification or Domain Name System (DNS)-based phishing. With a pharming scheme, hackers tamper with a company's hosts files or domain name system so that requests for URLs or name service return a bogus address and subsequent communications are directed to a fake site. The result: users are unaware that the website where they are entering confidential information is controlled by hackers and is probably not even in the same country as the legitimate website.
Content-Injection Phishing describes the situation where hackers replace part of the content of a legitimate site with false content designed to mislead or misdirect the user into giving up their confidential information to the hacker. For example, hackers may insert malicious code to log user's credentials or an overlay which can secretly collect information and deliver it to the hacker's phishing server.
Man-in-the-Middle Phishing is harder to detect than many other forms of phishing. In these attacks hackers position themselves between the user and the legitimate website or system. They record the information being entered but continue to pass it on so that users' transactions are not affected. Later they can sell or use the information or credentials collected when the user is not active on the system.
Search Engine Phishing occurs when phishers create websites with attractive (often too attractive) sounding offers and have them indexed legitimately with search engines. Users find the sites in the normal course of searching for products or services and are fooled into giving up their information. For example, scammers have set up false banking sites offering lower credit costs or better interest rates than other banks. Victims who use these sites to save or make more from interest charges are encouraged to transfer existing accounts and deceived into giving up their details.
Reference : http://www.pcworld.com/businesscenter/article/135293/types_of_phishing_attacks.html
Thursday, February 24, 2011
E-banking scams on the rise
References
Friday, February 18, 2011
Spear Phishing Trial in Canada
Thursday, February 17, 2011
Search Engine Phishing
1. Jessica Hunter, Search Engine Phishing-What you need to known, [Online], Retrieved on 16 February 2011.
URL: http://www.identitytheftfixes.com/search_engine_phishing_--_what_you_need_to_know.html
2. Robert Ma, Phishing Attack Detection by Using a Reputable Search Engine, [Online], Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of Toronto, Retrieved on 17 February 2011.
URL: http://www.eecg.toronto.edu/~lie/Courses/ECE1776-2006/Projects/Phishing2a-proposal.pdf
Monday, February 14, 2011
What is Phishing ?
1. 什么是“网络钓鱼”?,[Online], Retrieved on 14 February 2011.
URL: http://iask.sina.com.cn/b/12785184.html?from=related
Thursday, February 10, 2011
Poll week 2

Poll question of the second week, "Did you know more about phishing after reading this blog?". The result of 8 votes from our readers, 37.5% of them voted "I have gained a lot of knowledge", thanks for the vote and this blog is going to contribute wider information to you people. 12.5% of them voted "A little", and 50% of them voted "Normal", we'll continue gather more information about phishing in this blog.
Why phishing website still exist?
Mengikut statistik yang dikeluarkan pada tahun lepas, sebanyak 45% daripada 3 juta pengguna internet seluruh dunia tertipu dengan taktik laman web phishing ini.
- Do not click on links from a link provided via email.
- Communicate personal information only via phone or secure web sites.
- Check the url in the address bar. It is pointing to the right websites.
References:
Jmay, Kenapa laman web phishing masih wujud?,[Online], updates on 27 December 2010.
URL: http://www.jmayz.com/kenapa-laman-web-phishing-masih-wujud/
Sunday, February 6, 2011
What does a phishing E-mails look like ?
The link in this e-mail, which is suppose to go to eBay, actually goes somewhere else.You can see that this text is actually hiding a link to another site (66.246.90.60), as shown in the close up in Picture 2. And also, the original link text does not have a "https://" secure address, but if a link like this read "https://" you might think it was safe while it could actually be hiding a fake, non-secure URL. Picture 2 |
Thursday, February 3, 2011
Describe Phishing attacks
Phishing is one of the most common attack vectors used by hackers and social engineers to steal identities. Phishing involves sending an e-mail, usually posing as a bank, credit-card company, or other financial organization. The e-mail requests that the recipient confirm banking information or reset password or PIN numbers.
Phishing is the practice of sending fraudulent e-mail messages to addresses requesting them to supply confidential information. The e-mail is disguised to look like a request from a legitimate organization such as a thrift, or a credit card company. Victims may be directed to provide personal account information by responding to the e-mail. The hacker and social engineering is able to capture this information and use it for financial gain. The brief e-mails that addressed masses were no longer the most effective way to trick a victim into giving up their credentials.
Phishing PopUps- Fake Requests for Personal Financial Information,[Online],Retrieved 3 February 2011.
URL:http://www.consumerfraudreporting.org/phishingpopups.php
Tuesday, February 1, 2011
Facebook Phishing

This post is going to discuss about phishing in facebook. First, people will fall into phishing in facebook mainly because they have clicked into some link that sent by a phisher. Those message can be from e-mail, user wall or any website.
Ways to avoid from falling from facebook phishing.
- Choose a unique username and password for it, try not to set the same password for every accounts because this may cause you keep stolen information from compromising other accounts. (If it's too difficult for you to remember every single password from each site, I suggest to write a note and paste it beside the screen of your own personal computer)
- Always check the URL whenever you enter facebook.com, as I have stated earlier.
- Always update Anti-Virus Program for protecting your site from unknown virus.
- Remember facebook will not ask for re-enter password whenever you access to applications in facebook. (except: when you set a security question, send a virtual gift, or change your contact email.)
- Be extra aware of weird wall post, do not simply click on them unless you know very well where they go.
- Set a security question on your Facebook Account Setting page. For victims who have been phished, Facebook User Operations team needs you to answer to that question to let you back in your facebook account.
- Look for typo error!

1. Ryan McGeehan, No Phishing,[Online],Retrieved on 1 February 2011.
URL: http://blog.facebook.com/blog.php?post=14600297130
2. Pinoytek, How to Stay Away From Phishing Websites That Look Like Facebook?,[Online], Retrieved on 1 February 2011.
URL: http://pinoytek.net/internet/how-to-stay-away-from-phishing-website-that-looks-like-facebook
3. MIKE, Facebook Phishing Attack, [Online], Retrieved on 1 February 2011.
URL: http://gadgetsteria.com/2009/04/29/facebook-phishing-attack-uh-oh/#









